Lung cancer has traditionally been connected to smoking; however, in recent decades, there has been a large increase in instances among those who have never smoked. This phenomena has prompted researchers to look into other risk factors, such as environmental pollution, chemical exposure, and genetic predispositions, that may impact illness development.
In 2017, almost 1.57 million new cases were reported in men and over 900,000 in women, highlighting the global scope of the issue. These findings emphasize the need of knowing the numerous factors that may contribute to the development of lung cancer in persons with no history of smoking, including environmental pollution, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle variables.
Definition and Scope of the Problem
Lung cancer is defined as the uncontrolled proliferation of cells in lung tissue, which compromises respiratory function. Although tobacco remains the leading risk factor, 10% to 20% of confirmed cases occur in people who have never smoked. According to the aforementioned study, adenocarcinoma is the most prevalent subtype, particularly among women (59.7% of female cases), accounting for 45.6% of male cases.
CONTINUE READING NEXT PAGE
Got a white raised bump as you can see in the photo, kind of feels hard underneath. Should I be concerned?
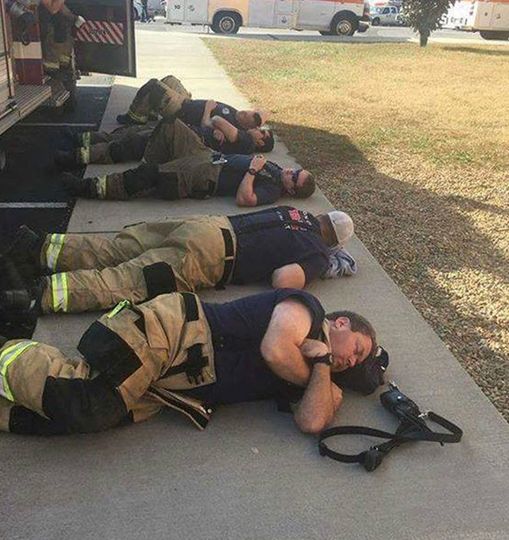
Man snaps heartbreaking photo of firefighters taking a rest after 24 hours of working nonstop
Why pour soda into the washing machine. Experienced housewives gave advice
Fried Egg Sandwich
Title: When Squeezing Lemons, Do Not Make the Mistake of Discarding the Seeds – They Are Worth Their Weight in Gold
I had no idea